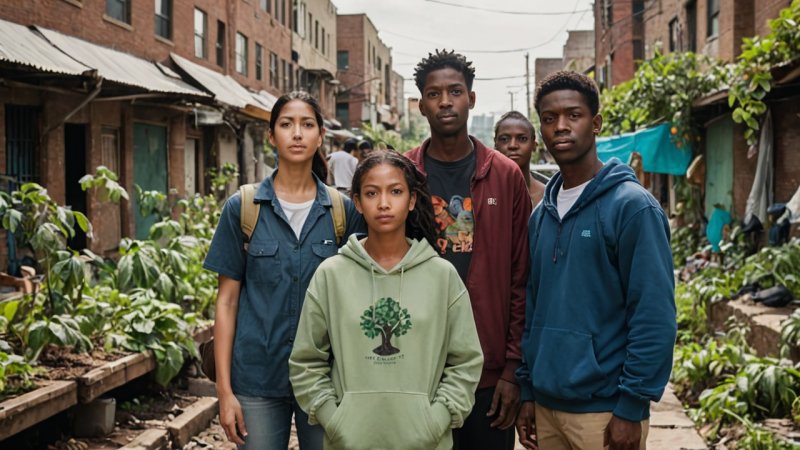
The phenomenon of climate refugees is becoming increasingly pressing as the world grapples with the consequences of climate change. With natural disasters, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events becoming more frequent, millions of people are being displaced from their homes. This article explores how academic research is tackling the challenges faced by climate refugees, shedding light on innovative solutions, policy implications, and the role of various disciplines in addressing this global crisis.
Understanding Climate Refugees
Climate refugees, often referred to as environmental migrants, are individuals who are forced to leave their homes due to sudden or gradual environmental changes that compromise their living conditions. These changes can include severe droughts, hurricanes, floods, and other climate-related events. According to the United Nations, it is estimated that by 2050, there could be as many as 200 million climate refugees worldwide. This staggering figure highlights the urgency of understanding the implications of climate change on human mobility.
The Role of Research in Identifying Trends
Academic research plays a critical role in identifying and analyzing trends related to climate refugees. Researchers from various fields, including environmental science, sociology, and economics, are working together to understand the factors driving displacement. For instance, studies have shown that regions with a high dependency on agriculture are particularly vulnerable to climate impacts, leading to increased migration as people seek more stable living conditions. By analyzing historical data and current trends, researchers can better predict future migration patterns and inform policymakers about potential hotspots for climate-induced displacement.
Innovative Solutions from Technology and Engineering
Technological advancements are also being harnessed to address the challenges faced by climate refugees. For example, researchers are developing early warning systems that utilize satellite imagery and data analytics to predict natural disasters and their potential impact on communities. These systems can provide crucial information to governments and NGOs, enabling them to prepare and respond more effectively to impending crises.
Furthermore, engineering solutions such as sustainable housing and resilient infrastructure are being explored. By designing homes that can withstand extreme weather conditions and creating urban spaces that can adapt to changing environments, researchers are working to minimize the risk of displacement.
Policy Implications and Social Sciences Research
Understanding the social implications of climate-induced migration is essential for developing effective policies. Social scientists are conducting research to explore the experiences of climate refugees and the challenges they face in their new environments. Issues such as access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities are critical for successful integration into host communities.
Moreover, research has highlighted the importance of international cooperation in addressing the needs of climate refugees. Policies must be developed that not only provide immediate relief but also promote long-term solutions, such as investment in climate-resilient infrastructure and support for communities that host climate-displaced individuals.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Several case studies provide insight into how research and policy can work together to support climate refugees. For example, in Bangladesh, a country highly vulnerable to climate change, various NGOs and government agencies have collaborated to create programs aimed at assisting displaced populations. These initiatives focus on providing vocational training, education, and mental health support, helping individuals rebuild their lives after displacement.
In contrast, other regions have struggled to effectively address the needs of climate refugees, often due to political instability or lack of resources. These case studies serve as important lessons for policymakers and researchers alike, emphasizing the need for proactive measures and collaborative approaches in addressing the challenges posed by climate change.
The Humanities Perspective
The humanities also play a vital role in understanding the cultural and emotional aspects of displacement. Literature, art, and history provide valuable insights into the human experience of migration and the resilience of communities facing environmental challenges. By studying narratives from climate refugees, researchers can shed light on the psychological impact of displacement and the importance of preserving cultural identity in the face of change.
Engaging Communities in Research
One of the most effective ways to address the challenges of climate refugees is to engage affected communities in the research process. Participatory research methods allow researchers to collaborate with displaced individuals, ensuring that their voices are heard and their needs are prioritized. This approach not only empowers communities but also leads to more effective and relevant solutions.
Conclusion
As the world continues to grapple with the consequences of climate change, the issue of climate refugees will only become more pronounced. Academic research is vital in understanding the complexities of this phenomenon and identifying innovative solutions to support displaced populations. By fostering collaboration across disciplines, engaging communities, and informing policy, researchers are working to address the challenges posed by climate refugees. The journey toward a more resilient and equitable future for those affected by climate change is ongoing, and it is essential that we continue to prioritize research and action in this critical area.