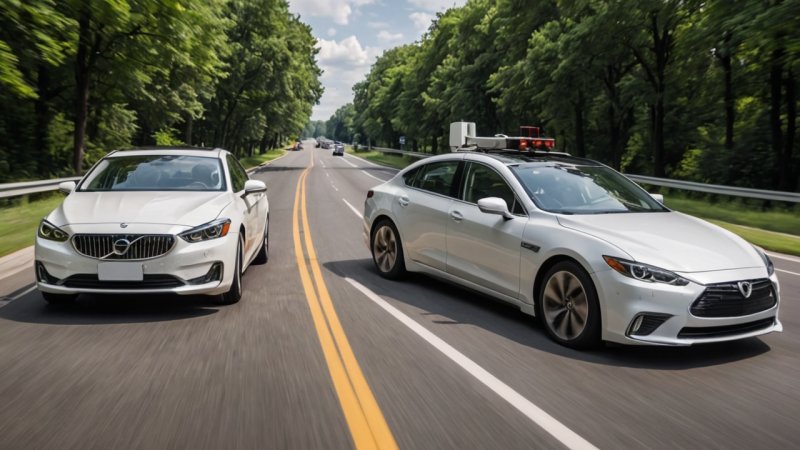
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the advent of autonomous vehicles (AVs). As technology advances, the debate between traditional vehicles and AVs becomes increasingly relevant. This article explores the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of both types of vehicles, shedding light on their impact on society, the environment, and the economy.
Definition and Overview
Traditional vehicles are those that require human drivers to operate, relying on human judgment and reflexes. In contrast, autonomous vehicles utilize advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), sensors, and machine learning to navigate roads without human intervention. Understanding these fundamental differences sets the stage for a deeper comparison.
Safety and Reliability
One of the most significant advantages of autonomous vehicles is their potential to enhance safety on the roads. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), over 90% of traffic accidents are caused by human error. AVs aim to reduce these incidents through precise calculations and real-time data analysis.
Pros of Autonomous Vehicles
- Reduced Accidents: By eliminating human error, AVs could significantly lower the number of accidents.
- Consistent Performance: AVs operate based on algorithms and data, ensuring consistent driving performance regardless of external conditions.
Cons of Autonomous Vehicles
- Technology Limitations: AVs may struggle with complex driving scenarios that require human intuition.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased reliance on technology raises concerns about hacking and data breaches.
Pros of Traditional Vehicles
- Human Judgment: Experienced drivers can make quick decisions in unpredictable situations.
- Established Infrastructure: Traditional vehicles are supported by existing road systems and regulations.
Cons of Traditional Vehicles
- Human Error: The possibility of accidents due to distraction or fatigue remains high.
- Inconsistent Performance: Drivers may react differently to similar situations, leading to unpredictable outcomes.
Environmental Impact
The environmental implications of vehicles are a crucial aspect of the ongoing discussion. Traditional vehicles, especially those powered by fossil fuels, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, many AVs are being designed with sustainability in mind, often incorporating electric powertrains.
Pros of Autonomous Vehicles
- Potential for Electric Integration: Many AVs are being developed as electric vehicles (EVs), which can reduce emissions.
- Improved Traffic Flow: AVs can communicate with each other to optimize traffic patterns, potentially reducing congestion and emissions.
Cons of Autonomous Vehicles
- Resource Intensive: The production of AVs, particularly their batteries, can be resource-intensive and environmentally damaging.
Pros of Traditional Vehicles
- Established Recycling Systems: The recycling of traditional vehicles is well-established, reducing waste.
Cons of Traditional Vehicles
- High Emissions: Traditional vehicles contribute to air pollution and climate change.
- Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Many traditional vehicles rely on non-renewable energy sources.
Economic Considerations
The economic impact of transitioning from traditional vehicles to autonomous ones is another critical factor. AVs promise to revolutionize industries such as transportation, logistics, and insurance, but they also pose challenges.
Pros of Autonomous Vehicles
- Cost Savings: AVs can reduce costs in logistics and delivery by optimizing routes and minimizing accidents.
- Job Creation in Tech: The development and maintenance of AV technology can create new job opportunities in tech and engineering.
Cons of Autonomous Vehicles
- Job Displacement: The rise of AVs may lead to job losses in driving professions.
- High Initial Investment: The cost of developing AV technology is substantial and may slow adoption.
Pros of Traditional Vehicles
- Established Market: The traditional automotive market is well-established, providing economic stability.
Cons of Traditional Vehicles
- Maintenance Costs: Traditional vehicles often incur higher maintenance costs due to wear and tear.
- Insurance Costs: Insurance premiums can be high due to the risk of accidents.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public acceptance of autonomous vehicles is a critical factor in their widespread adoption. Many people are still skeptical about the safety and reliability of AVs, while others embrace the potential benefits.
Pros of Autonomous Vehicles
- Innovative Appeal: AVs are seen as cutting-edge technology, appealing to tech-savvy consumers.
- Convenience: The potential for hands-free driving offers a level of convenience that traditional vehicles cannot match.
Cons of Autonomous Vehicles
- Skepticism: Many consumers are hesitant to trust technology over human drivers.
- Ethical Concerns: The ethical implications of AV decision-making in accident scenarios raise questions.
Pros of Traditional Vehicles
- Familiarity: Most consumers are comfortable with traditional vehicles and their operation.
Cons of Traditional Vehicles
- Resistance to Change: Some consumers may resist transitioning to new technologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between traditional vehicles and autonomous vehicles highlights significant differences in safety, environmental impact, economic considerations, and public perception. While autonomous vehicles offer promising advancements in safety and sustainability, challenges such as public skepticism and job displacement must be addressed. Ultimately, the future of transportation may not be a choice between the two but rather a coexistence that leverages the strengths of both traditional and autonomous technologies. As society moves forward, embracing innovation while considering ethical implications will be crucial for a successful transition.