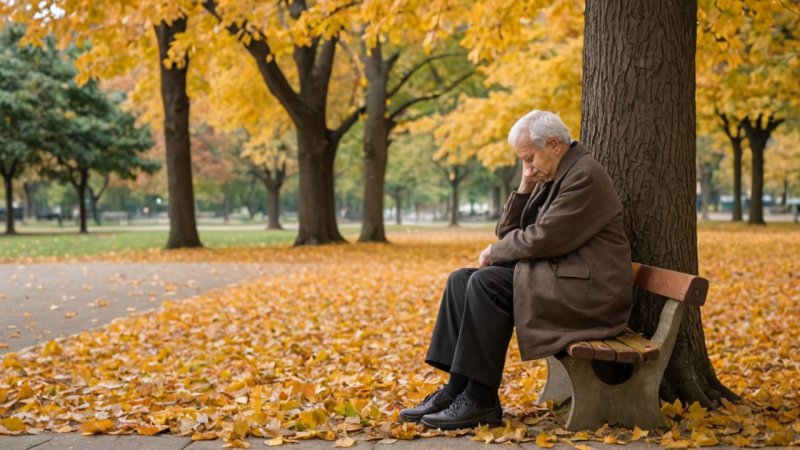
As the global population ages, the issue of social isolation among the elderly has gained increasing attention from researchers, caregivers, and policymakers alike. Social isolation can be defined as the lack of social connections and interactions, which can have profound effects on the mental and physical health of older adults. This article delves into the various dimensions of social isolation in the elderly, examining its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Understanding Social Isolation
Social isolation is a multifaceted phenomenon that can arise from a variety of factors, including physical disabilities, loss of loved ones, mobility limitations, and changes in living situations. For many elderly individuals, the transition to retirement can also lead to decreased social interactions, as they may no longer engage with colleagues or community groups. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated feelings of isolation, as many older adults were advised to stay home to avoid exposure to the virus.
Key Factors Contributing to Social Isolation
- Physical Health Issues: Chronic health conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, or cognitive decline can limit mobility and hinder social participation.
- Loss of Spouse or Friends: The death of close family members or friends can lead to loneliness and a shrinking social network.
- Relocation: Moving to assisted living facilities or nursing homes can disrupt established social ties.
- Technological Barriers: Many elderly individuals may struggle with technology, making it difficult to connect with others through digital platforms.
The Consequences of Social Isolation
The effects of social isolation on the elderly can be severe and far-reaching. Research has shown that social isolation is linked to numerous health risks, both mental and physical.
Mental Health Implications
Social isolation can lead to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Studies indicate that isolated seniors are at a higher risk of developing mental health disorders. The lack of social engagement can also hinder cognitive function, leading to a decline in memory and overall mental acuity.
Physical Health Risks
Beyond mental health, social isolation has been associated with a range of physical health issues. Isolated individuals may neglect their health, leading to poor nutrition, lack of exercise, and missed medical appointments. Research has shown that social isolation can increase the risk of conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and even premature death.
Addressing Social Isolation
Given the serious implications of social isolation, it is crucial to identify strategies to mitigate its effects. Various interventions can help foster social connections among elderly individuals.
Community Programs
Local communities can play a vital role in combating social isolation. Programs that encourage social interaction, such as senior centers, group activities, and volunteer opportunities, can help older adults build new relationships and maintain existing ones. These programs not only provide social engagement but also promote physical activity and mental stimulation.
Technology as a Tool
While technology can be a barrier for some seniors, it can also serve as a powerful tool for connection. Initiatives that provide training on using smartphones, tablets, and social media can empower older adults to stay in touch with family and friends, access online communities, and participate in virtual events.
Support from Family and Friends
Family members and friends can play a crucial role in reducing social isolation by making an effort to stay connected. Regular phone calls, video chats, and in-person visits can help elderly individuals feel valued and less alone. Additionally, organizing family gatherings or outings can provide opportunities for social interaction.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Examining successful interventions can provide valuable insights into effective strategies for combating social isolation in the elderly.
Example 1: The Village Movement
The Village Movement is a grassroots initiative that aims to create communities where older adults can age in place while maintaining social connections. Villages provide a network of support, including social activities, transportation services, and access to resources. This model has been successful in fostering a sense of belonging and reducing isolation among seniors.
Example 2: Technology Training Programs
Numerous organizations have implemented technology training programs specifically designed for seniors. These programs teach older adults how to use devices and platforms to connect with loved ones and engage in online activities. Participants often report increased confidence and a greater sense of connection to their communities.
Conclusion
Social isolation is a significant issue affecting the elderly population, with profound implications for their mental and physical health. Understanding the factors contributing to isolation and implementing effective strategies can help mitigate its effects. By fostering community connections, leveraging technology, and encouraging family involvement, we can create a more inclusive environment for older adults, ensuring they lead fulfilling and connected lives. Addressing social isolation is not just a health concern; it is a societal responsibility that requires collective action.