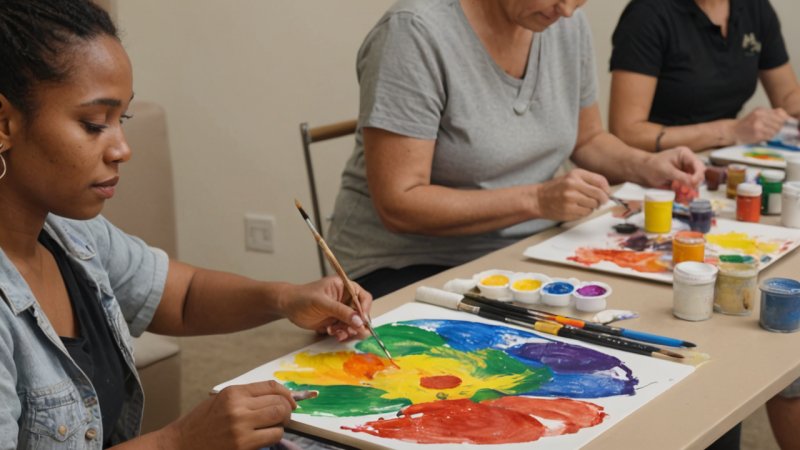
In recent years, the connection between art and mental health has garnered increasing attention from both researchers and practitioners. The therapeutic potential of artistic expression has been recognized not only as a means of personal exploration but also as a viable method for improving mental well-being. As society continues to navigate the complexities of mental health, understanding how art can play a role in healing is more crucial than ever. From painting and music to dance and drama, various forms of art have proven to be powerful tools for self-expression, emotional release, and community connection. This article delves into the multifaceted relationship between art and mental health, highlighting key studies, theories, and practices that illuminate this vital intersection.
Art as a Form of Expression
One of the most fundamental ways art contributes to mental health is through its capacity for expression. Many individuals struggling with mental health issues find it challenging to articulate their feelings verbally. Art provides an alternative medium through which they can express complex emotions that may be difficult to convey in words. For instance, a person dealing with anxiety might find solace in painting, using color and form to communicate feelings of chaos or calm. Various studies have highlighted that engaging in creative activities can lead to significant reductions in anxiety and depression symptoms. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Art Therapy Association, participants who engaged in art-making reported lower levels of distress and improved mood.
Art Therapy: A Structured Approach
Art therapy is a professional practice that combines the creative process of making art with psychological theory and techniques. This therapeutic approach is facilitated by trained art therapists who guide individuals in using art to explore their emotions, reduce anxiety, and improve overall mental health. Research has shown that art therapy can be particularly effective for individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety disorders. A notable study conducted by the University of California found that participants who underwent art therapy exhibited a significant decrease in PTSD symptoms compared to those who did not receive art therapy. The structured environment of art therapy allows individuals to explore their feelings in a safe space, fostering healing and self-discovery.
The Neurobiology of Art and Emotion
Understanding the neurobiological underpinnings of art and emotion can provide insight into why creative expression can have such profound effects on mental health. Engaging in artistic activities has been shown to activate various brain regions associated with emotion regulation, reward processing, and cognitive function. For example, a study published in the journal Neuropsychologia found that creating and viewing art can stimulate the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter linked to pleasure and reward. This biological response may explain why individuals often feel a sense of relief or joy after engaging in creative activities. Furthermore, art can serve as a form of mindfulness, allowing individuals to focus their attention and immerse themselves in the present moment, which is beneficial for mental health.
Community and Connection Through Art
Art also plays a significant role in fostering community and connection, both of which are essential for mental well-being. Participating in group art activities, such as community murals or theater productions, can create a sense of belonging and shared purpose. These collaborative experiences can reduce feelings of isolation and promote social interaction, which is particularly important for individuals facing mental health challenges. Research has indicated that social engagement through artistic endeavors can lead to improved mental health outcomes. For instance, a study published in the journal Arts & Health found that individuals who participated in community art projects reported increased feelings of social support and decreased loneliness.
Challenges and Considerations
While the relationship between art and mental health is largely positive, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind. Not all individuals may feel comfortable or capable of engaging in artistic expression, and the pressure to create “good” art can be counterproductive. It is essential to emphasize that the process of creating art is more important than the final product. Additionally, access to art therapy and community art programs can be limited, particularly in underserved areas. Advocating for increased access to these resources is crucial for ensuring that more individuals can benefit from the healing power of art.
Conclusion: Embracing Art for Mental Wellness
As we continue to explore the intricate relationship between art and mental health, it becomes clear that creative expression holds significant potential for healing and personal growth. Whether through structured art therapy or informal creative practices, engaging in art can provide individuals with a voice, a sense of community, and a pathway to emotional well-being. As research in this field evolves, it is vital to promote the integration of art into mental health care and to advocate for broader access to artistic resources. By embracing the therapeutic power of art, we can foster a more compassionate and supportive society that values mental wellness.