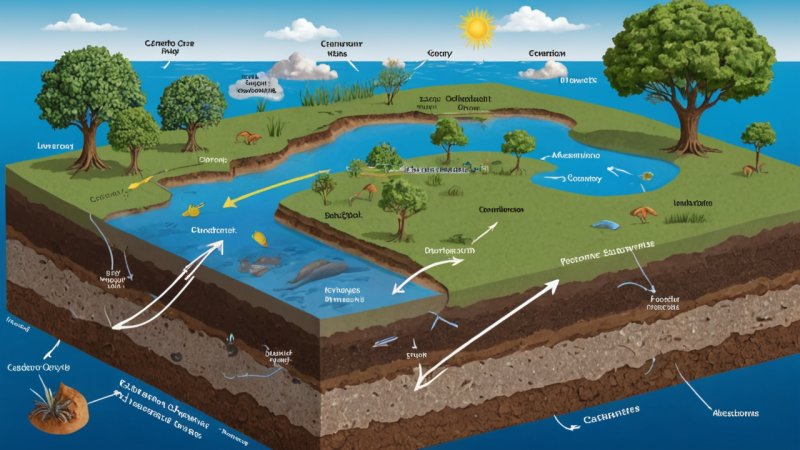
What is the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle is a natural process that describes how carbon atoms move through the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. It is an essential component of the Earth's ecosystem, playing a crucial role in regulating the planet's climate and supporting life.
Why is the carbon cycle important?
The carbon cycle is vital for several reasons:
- Climate Regulation: It helps regulate the Earth's temperature by controlling the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere.
- Life Support: Carbon is a fundamental building block of life, essential for the formation of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in living organisms.
- Soil Health: The carbon cycle contributes to soil fertility, supporting agriculture and natural ecosystems.
What are the main processes in the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle consists of several key processes:
- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic matter using sunlight.
- Respiration: Living organisms, including plants and animals, release CO2 back into the atmosphere through the process of respiration.
- Decomposition: When organisms die, decomposers break down their organic matter, releasing carbon back into the soil and atmosphere.
- Combustion: The burning of fossil fuels and biomass releases stored carbon into the atmosphere as CO2.
- Ocean Absorption: Oceans absorb a significant amount of CO2 from the atmosphere, which is utilized by marine life and also contributes to ocean acidification.
How does human activity affect the carbon cycle?
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes, have significantly altered the carbon cycle:
- Increased CO2 Levels: The combustion of fossil fuels releases large amounts of CO2, contributing to climate change.
- Deforestation: Cutting down forests reduces the number of trees available to absorb CO2, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Land Use Changes: Converting natural ecosystems into agricultural or urban areas disrupts the natural carbon storage processes.
What are the implications of climate change on the carbon cycle?
Climate change has several implications for the carbon cycle:
- Feedback Loops: As temperatures rise, permafrost thaws, releasing stored carbon and further accelerating climate change.
- Ocean Health: Increased CO2 levels lead to ocean acidification, affecting marine ecosystems and the organisms that rely on them.
- Altered Weather Patterns: Changes in temperature and precipitation can impact plant growth, affecting the natural absorption of CO2.
How can we mitigate the effects of human impact on the carbon cycle?
There are several strategies to mitigate human impact on the carbon cycle:
- Reduce Fossil Fuel Use: Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric can significantly lower CO2 emissions.
- Reforestation: Planting trees and restoring forests can enhance carbon absorption and help restore natural ecosystems.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing practices that improve soil health and reduce emissions can contribute to a more balanced carbon cycle.
What role does carbon capture technology play in the carbon cycle?
Carbon capture technology aims to capture CO2 emissions from industrial processes and store it underground or utilize it in other applications, thereby reducing the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere. This technology can play a significant role in mitigating climate change and restoring balance to the carbon cycle.
What can individuals do to help maintain the carbon cycle?
Individuals can contribute to maintaining the carbon cycle by:
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: Using public transport, biking, or walking instead of driving can lower personal emissions.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: Choosing products from companies that prioritize sustainability and environmentally friendly practices.
- Advocating for Policy Change: Supporting policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy sources.
In conclusion, understanding the carbon cycle and its implications is crucial for addressing climate change and promoting a sustainable future. By recognizing our role in this cycle and taking action, we can help mitigate the effects of human activity and support a healthier planet.