In recent years, the relationship between economic inequality and social stability has garnered increasing attention from researchers, policymakers, and the public alike. As wealth continues to concentrate in the hands of a few, questions arise about how this disparity impacts social cohesion and overall stability within societies. This article explores the key points surrounding this complex issue.
Economic inequality refers to the unequal distribution of wealth and resources among individuals or groups within a society. It can manifest in various forms, including income disparity, access to education, and healthcare availability. The consequences of such inequality can be profound, affecting not only the economic landscape but also social structures and relationships.
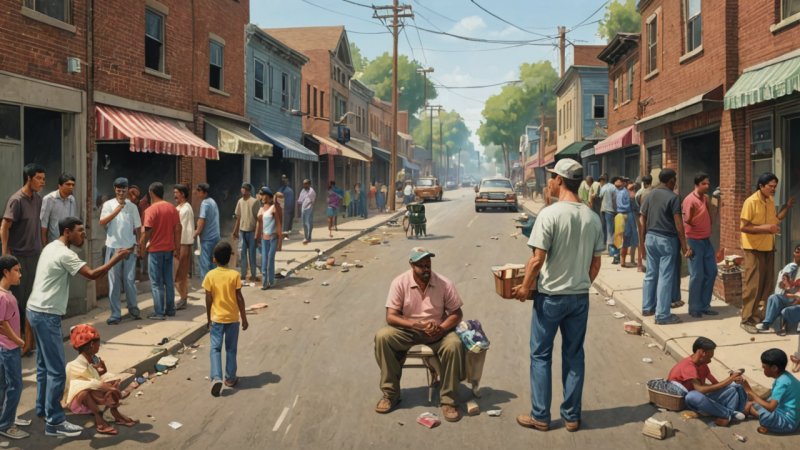
Research indicates that high levels of economic inequality can lead to increased social tensions. When a significant portion of the population feels marginalized or deprived of opportunities, it can foster resentment and distrust towards institutions and fellow citizens. This discontent can manifest in various ways, including protests, increased crime rates, and a general decline in civic engagement.
One key aspect of this relationship is the impact of inequality on social mobility. In societies with significant economic disparities, individuals from lower-income backgrounds often find it challenging to improve their circumstances. Limited access to quality education and job opportunities can create a cycle of poverty that is difficult to escape. This lack of upward mobility not only affects individuals but can also lead to broader societal issues, as entire communities may feel trapped in a system that favors the wealthy.
Moreover, economic inequality can undermine trust in institutions. When citizens perceive that the system is rigged in favor of the wealthy, they may lose faith in democratic processes and governance. This erosion of trust can lead to political instability, as individuals become disillusioned with their leaders and the political system itself. The result can be a vicious cycle where instability further exacerbates inequality, leading to a downward spiral.
Conversely, some argue that a certain level of economic inequality can be beneficial for motivating innovation and growth. The argument suggests that when individuals are rewarded for their efforts and contributions, it can drive progress and development. However, this perspective often overlooks the potential social costs associated with extreme inequality, such as social unrest and the breakdown of community bonds.
To address the challenges posed by economic inequality, various solutions have been proposed. Policy measures such as progressive taxation, increased access to education, and healthcare reform can help mitigate disparities and promote a more equitable society. Additionally, fostering inclusive economic growth that benefits all segments of the population can contribute to greater social stability.
In conclusion, the relationship between economic inequality and social stability is intricate and multifaceted. While some level of inequality may drive innovation, excessive disparities can lead to social unrest and political instability. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from governments, communities, and individuals to create a more equitable society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.