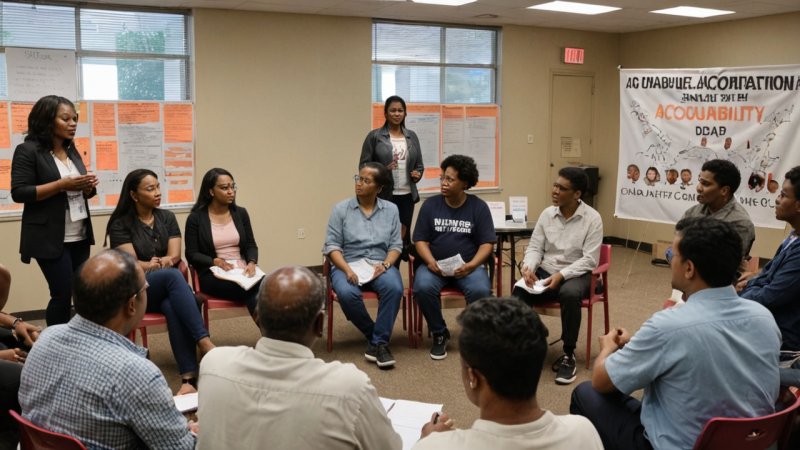
In recent decades, the role of civil society in promoting good governance has gained significant attention across the globe. Civil society refers to the organizations and institutions that operate independently from the government and the business sector, encompassing a wide range of entities such as non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community groups, and advocacy networks. These organizations are crucial in fostering transparency, accountability, and civic engagement, all of which are essential components of effective governance.
One of the primary ways civil society contributes to good governance is through advocacy and policy influence. Civil society organizations often serve as a voice for marginalized communities, bringing attention to issues that might otherwise be overlooked by policymakers. By conducting research, mobilizing public opinion, and engaging in dialogue with government officials, these organizations help ensure that the needs and concerns of citizens are reflected in public policies. For instance, organizations focused on environmental issues can advocate for sustainable practices, pushing governments to adopt policies that protect natural resources and promote ecological balance.
Transparency and accountability are other critical areas where civil society plays a vital role. Many civil society organizations monitor government activities, ensuring that public officials are held accountable for their actions. They achieve this through various means, including investigative journalism, public reporting, and grassroots mobilization. By shining a light on corruption and mismanagement, these organizations not only raise awareness but also empower citizens to demand better governance from their leaders.
Moreover, civil society organizations often provide essential services and support to communities, especially in areas where government resources are lacking. For example, NGOs may offer educational programs, healthcare services, or disaster relief efforts, directly impacting the lives of individuals and families. This grassroots approach not only addresses immediate needs but also builds trust between citizens and their governments, fostering a culture of collaboration and mutual support.
Another significant aspect of civil society's role in promoting good governance is its ability to facilitate dialogue and participation. Civil society organizations often serve as intermediaries between the government and the public, creating platforms for citizens to engage in discussions about governance and policy-making. By encouraging public participation, these organizations help ensure that diverse voices are heard, leading to more inclusive and representative decision-making processes.
In conclusion, civil society is a fundamental pillar in the promotion of good governance. By advocating for accountability, providing essential services, and facilitating public participation, civil society organizations play a crucial role in shaping policies that reflect the needs and aspirations of citizens. As we continue to navigate the complexities of governance in the 21st century, strengthening the capacity and influence of civil society will be vital to ensuring that governments remain responsive, transparent, and accountable to the people they serve.